Why is Modbus Still Alive in 2025? Discover the reasons why this 40-year-old industrial communication protocol continues to thrive in automation, IoT, and Industry 4.0.
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Legacy of Modbus
- A Brief History of Modbus
- The Core Features That Make Modbus Timeless
- Simplicity
- Openness
- Interoperability
- Cost-effectiveness
- Modbus Variants: Serial, TCP, and Beyond
- Why Industries Still Rely on Modbus in 2025
- Industrial Automation
- Energy & Utilities
- Building Automation
- Transportation & Infrastructure
- Agriculture & Smart Irrigation
- Modbus in the Age of IoT and Industry 4.0
- The Advantages of Modbus Over Newer Protocols
- Limitations of Modbus: Why Isn’t It Obsolete?
- Modbus Gateways, Converters, and Modern Adaptations
- Cybersecurity Challenges and Solutions for Modbus
- Case Studies: Real-World Use of Modbus in 2025
- The Future of Modbus: Coexistence with Modern Protocols
1. Introduction: The Legacy of Modbus
In the world of industrial automation and communication, technologies come and go. Proprietary systems vanish, new wireless standards emerge, and complex IoT protocols fight for dominance. Yet, one protocol, born in 1979, continues to stand strong even in 2025: Modbus.
For many, the survival of Modbus is surprising. Why would an almost 50-year-old protocol still be relevant when faster, more secure, and more advanced options exist? The answer lies in its simplicity, reliability, and adaptability.
This article explores why Modbus is still alive in 2025, its advantages, challenges, and how it continues to find a place in Industry 4.0, smart grids, and IoT ecosystems.
2. A Brief History of Modbus
Modbus was developed by Modicon (now Schneider Electric) in 1979 for programmable logic controllers (PLCs). It quickly became popular because it was:
- Open and free
- Simple to implement
- Vendor-neutral
Over the decades, Modbus expanded into different versions: Modbus RTU (serial), Modbus ASCII, and Modbus TCP/IP. Despite the emergence of modern protocols like EtherCAT, PROFINET, MQTT, and OPC UA, Modbus has never faded away.
3. The Core Features That Make Modbus Timeless
Simplicity
Modbus is easy to understand, implement, and debug. Engineers can set it up with minimal training. This is crucial in industries where downtime is costly.
Openness
Being an open protocol, Modbus does not require licensing fees. This lowers costs and makes it attractive to OEMs, integrators, and engineers worldwide.
Interoperability
Thousands of devices—sensors, meters, PLCs, and gateways—support Modbus. It acts as a universal language for equipment from different vendors.
Cost-effectiveness
Legacy equipment is expensive to replace. Modbus allows industries to extend the life of existing systems without massive reinvestment.
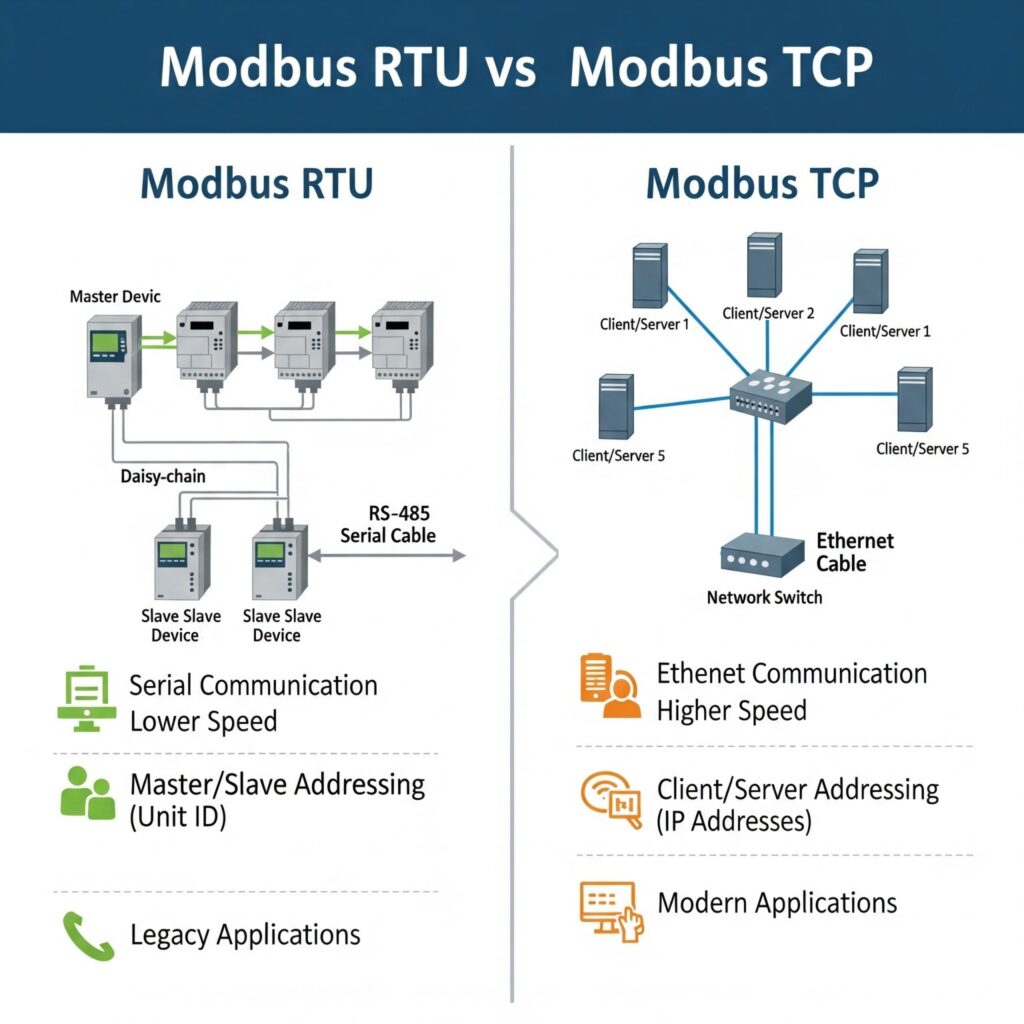
4. Modbus Variants: Serial, TCP, and Beyond
- Modbus RTU: Runs over RS-485 or RS-232. Still common in industrial plants and energy meters.
- Modbus ASCII: A less common version for serial communication.
- Modbus TCP/IP: Runs over Ethernet, making it compatible with modern networks.
- Modbus Plus and other hybrids: Adaptations for special use cases.
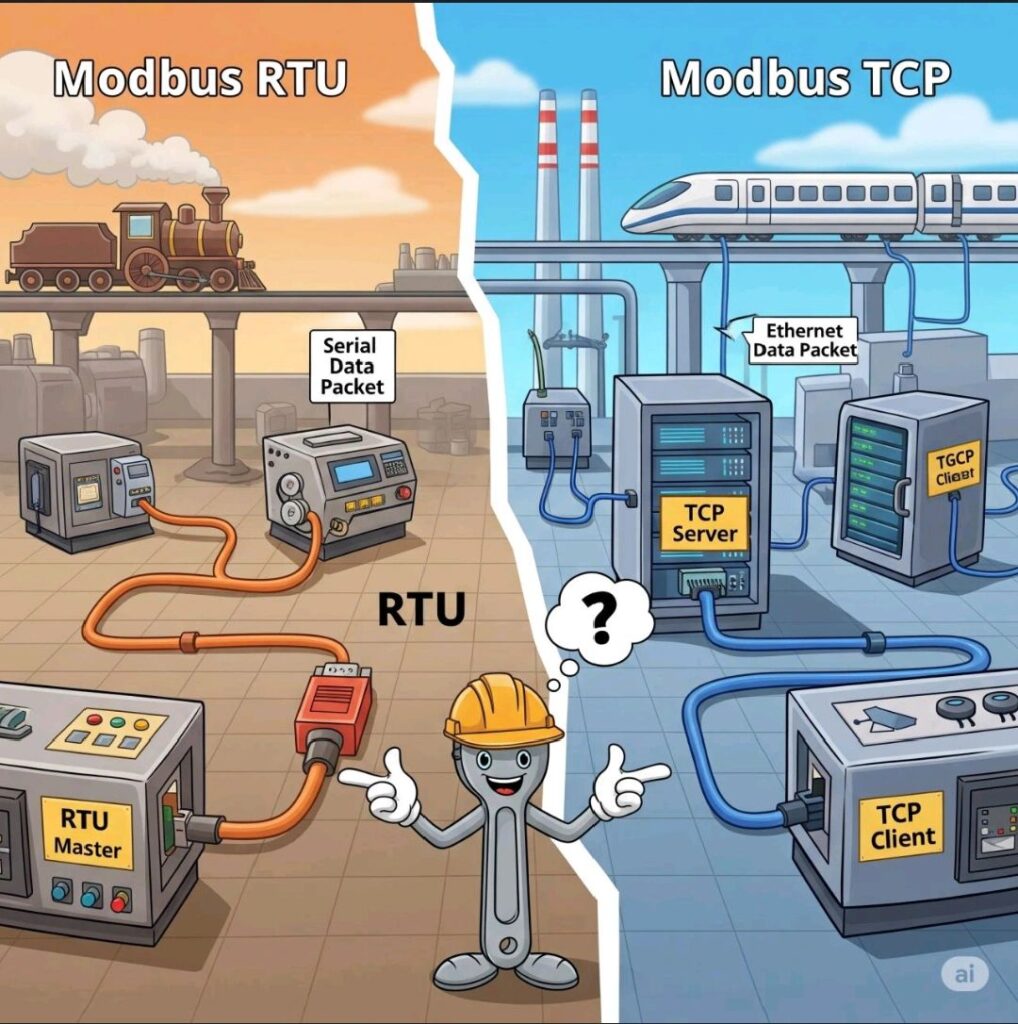
By 2025, Modbus TCP/IP has gained popularity, but Modbus RTU remains deeply entrenched in legacy equipment.
5. Why Industries Still Rely on Modbus in 2025
Industrial Automation
Factories continue using Modbus because PLCs, HMIs, and drives support it natively. It offers deterministic communication that is often enough for monitoring and control.
Energy & Utilities
Power plants, substations, and renewable energy farms rely on Modbus for metering and monitoring. Its simplicity makes it ideal for smart grids.
Building Automation
HVAC systems, lighting, elevators, and access control systems frequently use Modbus. It integrates well with BACnet and KNX.
Transportation & Infrastructure
Railway signaling, water treatment plants, and oil pipelines continue to use Modbus due to its ruggedness and reliability.
Agriculture & Smart Irrigation
Low-cost sensors and controllers in agriculture often use Modbus RTU because of its low power and low bandwidth requirements.
6. Modbus in the Age of IoT and Industry 4.0
At first glance, Modbus seems outdated for IoT. But with IoT gateways and cloud connectors, Modbus devices can now connect to MQTT brokers, OPC UA servers, and cloud platforms like AWS or Azure.
For example, a Modbus-based temperature sensor in a factory can feed data into an AI-driven predictive maintenance system via an edge gateway. This hybrid approach ensures that legacy devices are not left behind in the digital revolution.
7. The Advantages of Modbus Over Newer Protocols
- Widespread adoption – Almost every industrial device supports Modbus.
- Low cost of ownership – No licenses or expensive hardware.
- Ease of integration – Works well with SCADA systems.
- Reliability – Proven over decades in harsh conditions.
- Longevity – Existing infrastructure is difficult and costly to replace.
8. Limitations of Modbus: Why Isn’t It Obsolete?
Despite its strengths, Modbus has weaknesses:
- Limited speed and bandwidth (9600–115200 baud typical for RTU).
- Lack of advanced security (authentication, encryption).
- No standard for complex data types (compared to OPC UA).
- Master-slave structure (less flexible than publish-subscribe).
Yet, Modbus isn’t obsolete because its strengths outweigh its weaknesses in many practical scenarios.
9. Modbus Gateways, Converters, and Modern Adaptations
To bridge the old and new, protocol converters and gateways are widely used.
Examples include:
- RS485-to-USB converters for laptops.
- Modbus-to-MQTT gateways for IoT integration.
- Modbus-to-BACnet converters for building automation.
These solutions extend the life of Modbus devices while enabling integration with modern IT and OT systems.
10. Cybersecurity Challenges and Solutions for Modbus
Because Modbus lacks built-in security, it is vulnerable to:
- Spoofing attacks
- Data interception
- Unauthorized control commands
By 2025, solutions include:
- VPN tunneling and firewalls
- Secure Modbus over TLS
- Network segmentation
- Integration with cybersecurity frameworks
This balance allows Modbus to remain useful while minimizing risks.
11. Case Studies: Real-World Use of Modbus in 2025
Case Study 1: Solar Energy Farm
A 500 MW solar plant in India uses Modbus RTU over RS-485 to monitor inverters and weather stations. Data is aggregated via Modbus TCP and sent to a cloud-based dashboard.
Case Study 2: Smart Building in Europe
A commercial building in Germany integrates HVAC, lighting, and metering systems through Modbus. A gateway translates data into BACnet/IP for building management software.
Case Study 3: Water Treatment Plant in the U.S.
Critical pumps and valves run on PLCs communicating over Modbus RTU. A cybersecurity wrapper ensures safe data transmission.
12. The Future of Modbus: Coexistence with Modern Protocols
Rather than disappearing, Modbus is coexisting with newer protocols. It plays the role of a foundation layer, especially for legacy equipment, while gateways and middleware bridge the gap to IoT, AI, and advanced analytics.
In 2030 and beyond, Modbus may not dominate, but it will continue to silently power critical infrastructure, much like TCP/IP does for the internet.
So, why is Modbus still alive in 2025?
Because it is simple, cost-effective, universal, and adaptable. Despite its age and limitations, industries worldwide continue to rely on Modbus as the backbone of industrial communication. With the help of gateways, IoT integration, and cybersecurity enhancements, Modbus has transformed from a legacy protocol into a bridge between the past and the future of automation.
In other words, Modbus is not just alive in 2025—it is thriving.