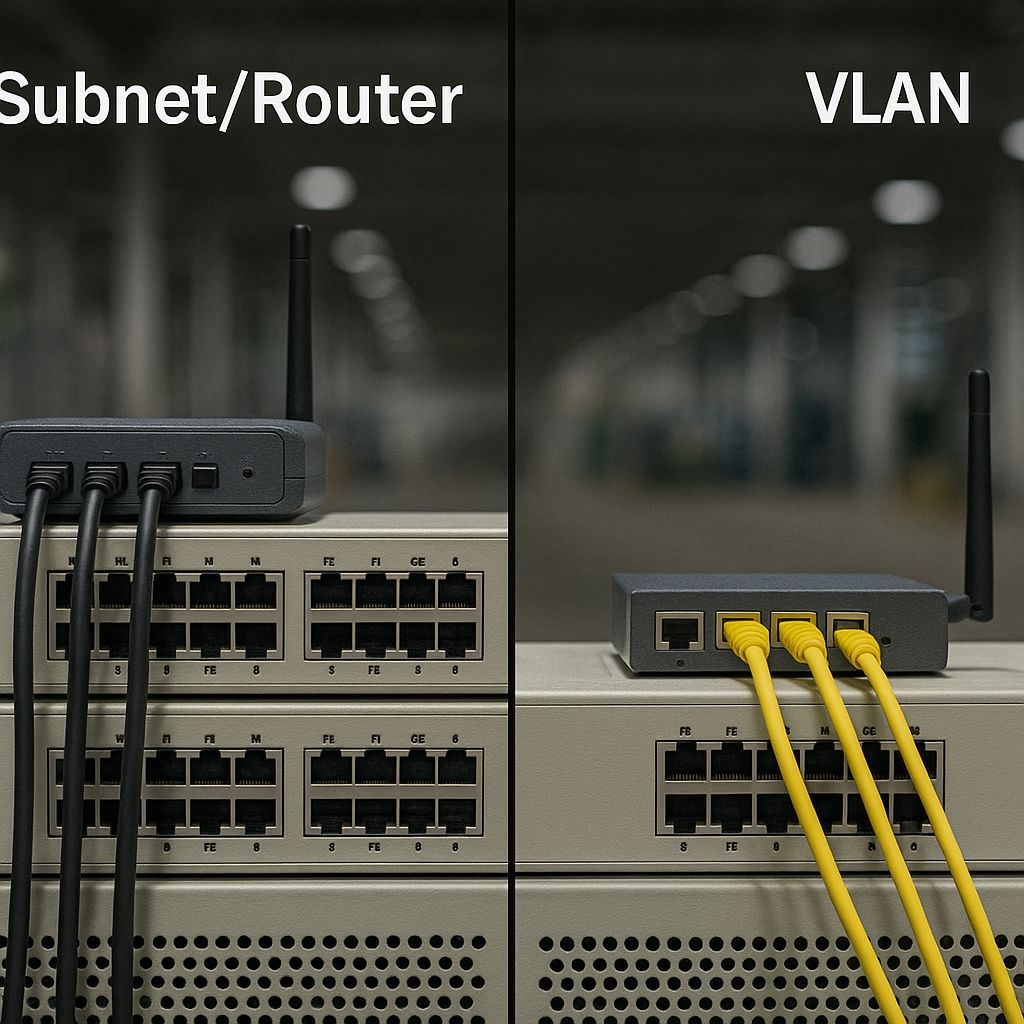
Discover the key differences between VLAN and Subnetting for OT environments. Learn which network segmentation method offers better security, scalability, and performance in Industry 4.0.
Introduction
When it comes to OT networks, a critical question arises: VLAN vs. Subnetting – which is the better network segmentation for our OT environments? Proper network segmentation is essential for security, performance, and reliability, especially in Industry 4.0 and IIoT setups. In this guide, we’ll break down both VLANs and Subnetting, compare their advantages, and help you determine the best approach—or combination—to optimize your OT network.
What is VLAN?
A VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) is a logical grouping of devices within a physical network. It allows administrators to segment traffic without requiring separate physical hardware.
- Key Features of VLAN:
- Logical network segmentation on Layer 2 (Data Link layer)
- Simplifies management of broadcast domains
- Provides flexibility for grouping devices across different switches
- Enhances security by isolating network traffic
(📌 Suggested Image: Diagram showing VLANs separating traffic on a switch.)
What is Subnetting?
Subnetting divides an IP network into smaller, more manageable sub-networks at Layer 3 (Network layer). This method ensures efficient use of IP addresses and better control over traffic flow.
- Key Features of Subnetting:
- Logical IP-based segmentation
- Helps optimize IP address allocation
- Limits broadcast traffic by creating multiple networks
- Essential for routing and inter-network communication
(📌 Suggested Image: Example of subnetting an IP network into smaller networks.)
VLAN vs. Subnetting – The Core Differences
| Feature | VLAN | Subnetting |
|---|---|---|
| OSI Layer | Layer 2 (Data Link) | Layer 3 (Network) |
| Segmentation Type | Logical grouping within switches | IP-based network division |
| Security | Provides traffic isolation | Controls traffic with routing rules |
| Scalability | Easy to expand within a LAN | Scales better across larger networks |
| Broadcast Control | Reduces broadcast domains | Each subnet has its own broadcast domain |
| Best Use Case | Internal LAN segmentation | Wide network segmentation & routing |
Which is Better for OT Environments?
When evaluating VLAN vs. Subnetting – which is the better network segmentation for our OT environments?, we need to consider the unique requirements of OT networks such as:
- Security Needs
- VLANs provide isolation at the switch level, which helps prevent unauthorized access.
- Subnetting adds another layer of control by enabling routing and firewall rules.
- Network Scalability
- VLANs are ideal for segmenting devices within the same LAN.
- Subnetting works better when OT devices need to connect across larger, distributed environments.
- Performance Optimization
- VLANs reduce broadcast traffic within a local network.
- Subnetting reduces unnecessary traffic across wide areas by defining boundaries.
- Compliance & Industry Standards
- Many Industry 4.0 and IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things) setups prefer using both VLANs and Subnetting together for layered security and compliance.
Best Practice: VLAN + Subnetting Together
The reality is that both VLAN and Subnetting are complementary. In most modern OT environments, network engineers use VLANs for local segmentation and Subnetting for hierarchical IP management and routing.
For example:
- Use VLANs to isolate PLCs, HMIs, and SCADA systems within the same plant floor.
- Use Subnetting to organize different OT zones (production, safety systems, remote monitoring) with better control over traffic flow.
Conclusion
When evaluating VLAN vs. Subnetting – which is the better network segmentation for our OT environments?, the answer depends on your specific network needs:
- VLANs excel in providing local traffic isolation, improved security, and simplified management within plant-floor networks.
- Subnets are ideal for scalable IP-based segmentation, routing control, and multi-site OT networks.
- For most modern OT and Industry 4.0 environments, the best approach is a combination of both VLANs and Subnetting, allowing layered segmentation, enhanced security, and optimal performance.
By carefully planning your network segmentation strategy using both VLANs and Subnets, you can ensure a secure, efficient, and future-ready OT network that meets Industry 4.0 standards and IIoT requirements.