Medium Voltage (MV) switchgear is one of the most important components in modern power distribution systems. It ensures the safe control, protection, and isolation of electrical equipment operating typically between 1 kV and 52 kV. Whether in industrial plants, commercial buildings, utilities, or renewable energy installations, MV switchgear plays a critical role in maintaining electrical reliability and preventing faults.
This comprehensive guide explains everything about AIS, GIS, VCB, RMU, and MV Protection Systems, updated to reflect 2025 technology trends, safety standards, and engineering practices.
Table of Contents
- What Is Medium Voltage Switchgear?
- Voltage Range & Global Standards
- Components of MV Switchgear
- Types of MV Switchgear (AIS, GIS, Hybrid)
- Vacuum Circuit Breakers (VCB)
- Ring Main Units (RMU)
- MV Protection Systems & Relays
- Switchgear Installation Requirements
- MV Switchgear Safety Procedures
- Maintenance & Condition Monitoring
- Applications of MV Switchgear
- Latest Trends in MV Switchgear (2025 Update)
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Conclusion
1. What Is Medium Voltage Switchgear?
Medium Voltage switchgear is an electrical assembly used to control, protect, and isolate electrical equipment at medium voltage levels. It includes devices like:
- Circuit breakers
- Disconnectors
- Busbars
- Protection relays
- Instrument transformers
- Earthing switches
Functions of MV Switchgear
- Protection from short circuits and overloads
- Switching of loads and feeders
- Isolation of faulty sections
- Measurement and metering
- Ensuring safe maintenance
Without MV switchgear, power distribution systems would be unsafe, unstable, and prone to catastrophic failures.
2. Voltage Range & Global Standards
MV switchgear typically handles 1 kV to 52 kV, depending on the region.
Common MV Voltage Levels
- 3.3 kV
- 6.6 kV
- 11 kV
- 22 kV
- 33 kV
- 36 kV
- 52 kV
Standards Governing MV Switchgear
- IEC 62271 series – Global standard for HV/MV switchgear
- IEEE C37 – U.S. switchgear standard
- ANSI standards – For American system designs
- IS/BS standards – For India and UK
3. Components of MV Switchgear
A complete switchgear assembly includes:
1. Circuit Breakers
For interrupting fault currents.
2. Busbars
Carry and distribute electrical power.
3. Current Transformers (CTs)
Measure current and provide input to relays.
4. Voltage Transformers (VTs/PTs)
Used for metering and protection.
5. Earthing Switch
Provides safe grounding during maintenance.
6. Protection Relays
Detect faults and operate breakers quickly.
7. Interlocks
Prevent unsafe operations.
8. Enclosure
A metal-clad or gas-insulated housing.
4. Types of MV Switchgear
Medium Voltage switchgear is classified based on its insulation method and construction.
A. Air-Insulated Switchgear (AIS)
AIS is the most common type of switchgear. The insulation between live parts is air.
Advantages
- Cost-effective
- Easy to maintain
- Simple design and construction
- Suitable for indoor substations and industrial plants
Disadvantages
- Requires larger footprint
- Sensitive to dust, pollution & humidity
Applications
- Utilities
- Manufacturing plants
- Commercial buildings
B. Gas-Insulated Switchgear (GIS)
GIS uses SF₆ gas or alternative eco-friendly gases as the primary insulating medium.
Advantages
- Very compact
- High reliability
- Excellent insulation
- Minimal maintenance
Disadvantages
- More expensive than AIS
- SF₆ gas is a greenhouse gas (strict handling rules)
Applications
- Urban substations
- Underground substations
- Offshore platforms
- Renewable energy installations
C. Hybrid Switchgear
A combination of AIS and GIS technologies.
Benefits
- Reduced space requirement
- Lower cost than full GIS
- Improved reliability
5. Vacuum Circuit Breakers (VCB)
Vacuum Circuit Breakers are the most widely used breakers in MV applications.
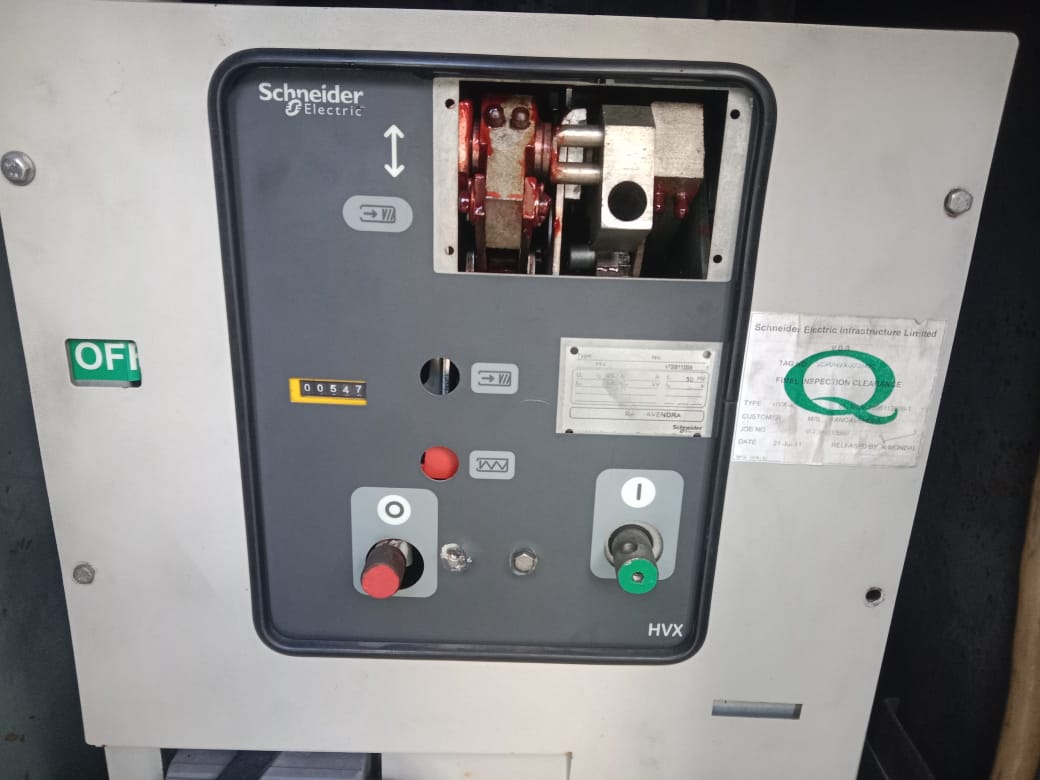

Why Vacuum Technology?
- High dielectric strength
- No gas handling
- Minimal maintenance
- Long mechanical life
How VCB Works
The arc is extinguished inside a vacuum interrupter. With no gases present, the arc collapses instantly.
Advantages
- Environment-friendly
- Suitable for 3.3 kV to 36 kV
- Long life (20,000+ operations)
Applications
- Industrial power distribution
- Large motors and transformers
- Utility substations
6. Ring Main Unit (RMU)
RMU is a compact, sealed switchgear used widely in 11 kV and 22 kV distribution networks.
Typical RMU Components
- Load break switches
- Circuit breaker
- Earth switch
- Busbar
- Feeder connections
Why RMUs Are Important
- Allow looped distribution
- Improve supply reliability
- Compact & maintenance-free
- Suitable for underground cable networks
Applications
- Urban distribution
- Solar/wind farms
- Commercial complexes
- Industrial estates
7. MV Protection Systems & Relays
Protection systems detect abnormal conditions and isolate the faulty section.
Types of Protection Relays
1. Overcurrent Relay (OCR)
Trips when current exceeds set value.
2. Earth Fault Relay (EFR)
Detects ground faults.
3. Differential Relay
Protects transformers, cables, and busbars.
4. Distance Relay
Used in long-distance feeders.
5. Under/Over Voltage Protections
6. Numerical Relays (IEDs)
Modern digital relays with communication capabilities:
- SCADA integration
- IEC 61850 GOOSE messaging
- Remote control
8. Switchgear Installation Requirements
Proper installation ensures safety and reliability.
Site Requirements
- Dust-free, ventilated environment
- Adequate clearances
- Level flooring
- Proper earthing system
Cable Entry Options
- Bottom entry
- Top entry
- Cable trench
Environmental Considerations
- Humidity control
- Temperature monitoring
- Vibration isolation
9. MV Switchgear Safety Procedures
Safety is the highest priority when working with MV systems.
Key Safety Rules
- Use LOTO (Lockout Tagout)
- Verify absence of voltage
- Wear arc flash PPE
- Ensure proper interlocks
- Keep safe distance
- Avoid unauthorized access
Arc Flash Hazards
Arc flash can cause:
- Burns
- Explosions
- Equipment damage
Preventive measures include:
- Infrared inspections
- Protective relays
- Arc flash reduction systems
10. Maintenance & Condition Monitoring
Proper maintenance avoids failures and extends equipment lifespan.
Maintenance Types
1. Preventive Maintenance
Regular inspections, cleaning, tightening.
2. Predictive Maintenance
Using condition-based tools like:
- Partial discharge sensors
- Thermal cameras
- Vibration monitors
3. Corrective Maintenance
Repair after failure.
Maintenance Checklist
- CT/VT testing
- Breaker mechanism lubrication
- Insulation tests
- Contact resistance measurement
11. Applications of MV Switchgear
MV switchgear is used across many industries.
Industrial Plants
- Steel
- Cement
- Chemical
- Automotive
Commercial Projects
- Airports
- Hospitals
- Data centers
Utility Distribution
- Feeder control
- Substations
Renewable Energy Projects
- Solar power plants
- Wind farms
- Battery energy storage systems (BESS)
12. Latest Trends in MV Switchgear (2025 Update)
1. SF₆-Free Switchgear
Eco-friendly alternatives:
- g³ gas
- Vacuum insulation
2. Digital Switchgear
Real-time monitoring:
- IoT sensors
- Cloud dashboards
- AI-based predictive maintenance
3. Compact Modular Switchgear
Used for:
- Smart cities
- Underground substations
4. Arc-Resistant Switchgear
Enhances operator safety.
5. Intelligent Electronic Devices (IEDs)
Advanced protection & automation.
6. Solid-State Circuit Breakers
Ultra-fast interruption technology.
13. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What is the main purpose of MV switchgear?
To control, protect, and isolate medium voltage circuits.
Q2: Which is better—AIS or GIS?
GIS is compact and reliable but more expensive. AIS is economical and easier to maintain.
Q3: Why are VCBs widely used in MV systems?
They offer high reliability, minimal maintenance, and long life.
Q4: What is an RMU used for?
RMU ensures looped distribution and improves network reliability.
Q5: What is the most common MV protection relay?
Numerical relays (IEDs) due to advanced features and communication support.
14. Conclusion
Medium Voltage switchgear is the backbone of modern power distribution systems. Understanding AIS, GIS, VCB, RMU, and protection systems is essential for designing, operating, and maintaining safe and reliable electrical networks. With the rise of digitalization, smart grids, and renewable energy, MV switchgear is evolving rapidly—becoming more compact, intelligent, and environmentally friendly.
Whether you are an engineer, technician, contractor, or facility manager, this guide provides the knowledge needed to make informed decisions about MV switchgear selection, installation, protection, and maintenance.